durvalumab
Durvalumab
is a monoclonal antibody medication used in the treatment of cancer. It works
by blocking the activity of a protein called PD-L1, which helps cancer cells
evade the immune system. Durvalumab is used to treat several types of cancers,
including non-small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, and head and neck cancer.
What is the drug durvalumab used for?
Durvalumab
is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of
several types of cancer, including:
Non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Durvalumab is used as a treatment for NSCLC in
combination with tremelimumab, another immunotherapy drug.
Bladder
cancer: Durvalumab is used to treat advanced bladder cancer that has come back
or worsened after prior treatment.
Head and
neck cancer: Durvalumab is used to treat recurrent or metastatic head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma.
In
addition to these FDA-approved uses, Durvalumab is also being studied in
clinical trials for the treatment of other types of cancer, including breast
cancer, prostate cancer, and liver cancer.
It is
important to note that Durvalumab may not be appropriate for everyone, and its
use must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis by a qualified healthcare
provider. Common side effects of Durvalumab can include fatigue, cough, and
shortness of breath, as well as more serious side effects such as severe
allergic reactions and changes in liver function.
Is durvalumab a chemo drug?
Durvalumab
is not a chemotherapy drug. Chemotherapy is a sort of cancer behavior that employs
drugs to slay cancer cells. Durvalumab is a type of immunotherapy, which works
differently from chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
is a form of treatment that uses the body's own immune system to fight cancer.
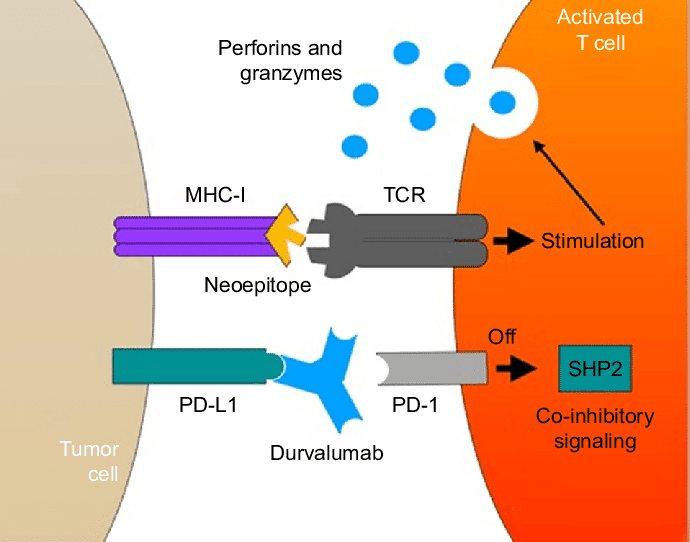
Durvalumab specifically is a monoclonal antibody, a type of protein that is
designed to target and block specific proteins found on the surface of cancer
cells. In the case of Durvalumab, it blocks the activity of PD-L1, a protein
found on the surface of cancer cells that helps them evade the immune system.
By blocking PD-L1, Durvalumab allows the immune system to recognize and attack
the cancer cells more effectively.
While
chemotherapy and immunotherapy are different types of cancer treatment, they
can sometimes be used together to help improve the overall effectiveness of treatment.
The best course of treatment depends on a variety of factors, including the
type and stage of cancer, overall health of the patient, and potential side
effects of each treatment. Your doctor can help you determine which type of
treatment is right for you.
Is durvalumab chemotherapy or immunotherapy?
Durvalumab
is a type of immunotherapy, not chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
is a form of cancer treatment that uses the body's own immune system to fight
cancer. Durvalumab specifically is a monoclonal antibody, a type of protein
that is designed to target and block specific proteins found on the surface of
cancer cells. In the case of Durvalumab, it blocks the activity of PD-L1, a
protein found on the surface of cancer cells that helps them evade the immune
system. By blocking PD-L1, Durvalumab allows the immune system to recognize and
attack the cancer cells more effectively.
In
contrast, chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill
cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs work by killing rapidly dividing cells,
including both cancer cells and normal cells that divide rapidly, such as cells
in the bone marrow, hair follicles, and the lining of the mouth and
gastrointestinal tract.
While
immunotherapy and chemotherapy are different types of cancer treatment, they
can sometimes be used together to help improve the overall effectiveness of
treatment. The best course of treatment depends on a variety of factors,
including the type and stage of cancer, overall health of the patient, and
potential side effects of each treatment. Your doctor can help you determine
which type of treatment is right for you.
What kind of drug is durvalumab?
Durvalumab
is a type of monoclonal antibody drug used in the treatment of cancer.
Monoclonal
antibodies are laboratory-made proteins that are designed to target specific
proteins found on the surface of cancer cells. They work by blocking the
activity of these proteins, thereby allowing the immune system to recognize and
attack the cancer cells more effectively.
In the
case of Durvalumab, it is designed to block the activity of PD-L1, a protein
found on the surface of cancer cells that helps them evade the immune system.
By blocking PD-L1, Durvalumab allows the immune system to recognize and attack
the cancer cells more effectively.
Durvalumab
is administered intravenously (into a vein) and can be given alone or in
combination with other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation
therapy.
It is
important to note that Durvalumab may not be appropriate for everyone, and its
use must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis by a qualified healthcare
provider. Common side effects of Durvalumab can include fatigue, cough, and
shortness of breath, as well as more serious side effects such as severe
allergic reactions and changes in liver function.








0 Comments